 |
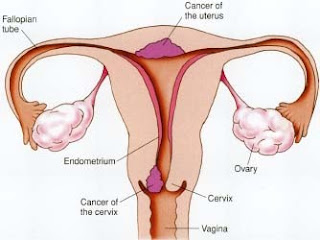
| Anatomy of Uterus, Cervix and Ovary |
1.Human pappiloma virus infection. Especially oncogenic subtypes type 16 and 18.
2.Coitarche at a younger age
3.Time gap between the menarche and the coitarche is less.
4.Multiple sexual partners
5.Multiparity
6.Immunosuppression eg. HIV infection, post-transplant
7.Smoking
8.Lower socioeconomic group.
Risk factors for the carcinoma of the endometrium
1.Age highest incidence in the postmenopausal age group in the 6th decade.
2.Increased exposure to the endogenous estrogens- early menarche, late menopause,nullipartiy, obesity, cirrhosis
3.Oestrogen secreting ovarian tumors- granulosa cell tumour.
4.Polycystic ovarian syndrome
5.Hypertension, diabetes mellitus
6.Endometrial hyperplasia with atypical changes
7.Exposure to unopposed oestrogen therapy as hormone replacement therapy.
8.Tamoxifen therapy- (in breast carcinoma treatment)
Risk factors for the carcinoma of the ovary
1.Ovulation induction therapy used in the treatment of subfertiliy due to anovulatory cycles.- eg. clomiphene
2.Family history of ovarian, breast or colonic cancers. Associated with BRCA 1 and BRCA 2 gene mutations and hereditary non polyposis colorectal cancer syndrome
3.Personal history of breast cacinoma. ( around 10% of ovarian cancers are familial and 90% sporadic)
4.Nulliparity, early menarche, late menopause, having the first child after 30. ( all share increased life time exposure to ovulatory cycles)
Breast feeding and consumption of combine hormonal contraception have a protective effect.

